Pancreastatin can regulate glucose tolerance, insulin sensitivity and its blood levels
Abstract
Discovery of pancreastatin inhibitor PSTi8 for the treatment of insulin resistance and diabetes: studies in rodent models of diabetes mellitus.
Pancreastatin (PST) is an endogenous peptide which regulates glucose and lipid metabolism in liver and adipose tissues. In type 2 diabetic patients, PST level is high and plays a crucial role in the negative regulation of insulin sensitivity. Novel therapeutic agents are needed to treat the diabetes and insulin resistance (IR) against the PST action. In this regard, we have investigated the PST inhibitor peptide-8 (PSTi8) action against diabetogenic PST. PSTi8 rescued PST-induced IR in HepG2 and 3T3L1 cells. PSTi8 increases the GLUT4 translocation to cell surface to promote glucose uptake in L6-GLUT4myc cells. PSTi8 treatment showed an increase in insulin sensitivity in db/db, high fat and fructose fed streptozotocin (STZ) induced IR mice. PSTi8 improved the glucose homeostasis which is comparable to metformin in diabetic mice, characterized by elevated glucose clearance, enhanced glycogenesis, enhanced glycolysis and reduced gluconeogenesis. PST and PSTi8 both were docked to the GRP78 inhibitor binding site in protein-protein docking, GRP78 expression and its ATPase activity studies. The mechanism of action of PSTi8 may be mediated by activating IRS1/2-phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase-AKT (FoxO1, Srebp-1c) signaling pathway. The discovery of PSTi8 provides a promising therapeutic agent for the treatment of metabolic diseases mainly diabetes.
Hossain Z, Valicherla GR, Gupta AP, et al. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):8715.
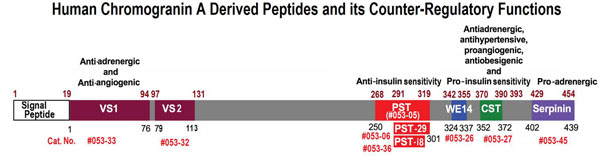
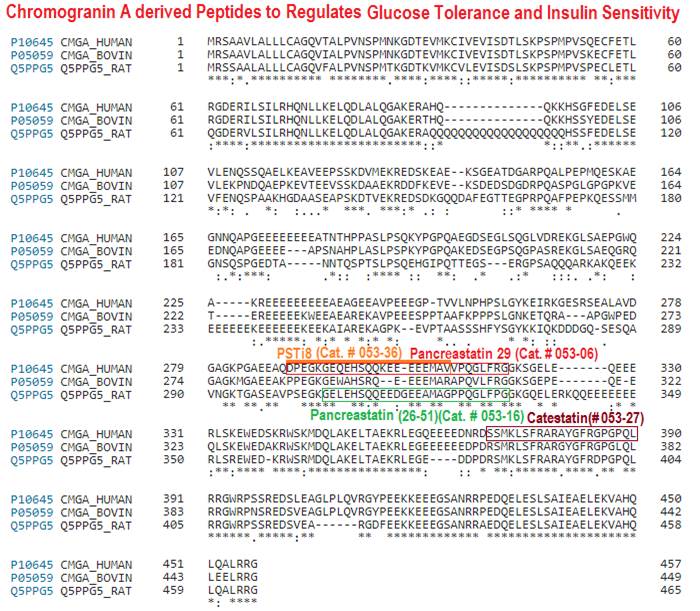
Chromogranin A (CgA) is a prohormone and granulogenic factor in endocrine and neuroendocrine tissues, as well as in neurons, and has a regulated secretory pathway. The intracellular functions of CgA include the initiation and regulation of dense-core granule biogenesis and sequestration of hormones in neuroendocrine cells. This protein is co-stored and co-released with secreted hormones. The extracellular functions of CgA include the generation of bioactive peptides, such as pancreastatin (PST), vasostatin, WE14, catestatin (CST), and serpinin. CgA knockout mice (Chga-KO) display: (i) hypertension with increased plasma catecholamines, (ii) obesity, (iii) improved hepatic insulin sensitivity, and (iv) muscle insulin resistance. These findings suggest that individual CgA-derived peptides may regulate different physiological functions. Indeed, additional studies have revealed that the pro-inflammatory PST influences insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance, whereas CST alleviates adiposity and hypertension. This review will focus on the different metabolic roles of PST and CST peptides in insulin-sensitive and insulin-resistant models, and their potential use as therapeutic targets.
Bandyopadhyay GK, Mahata SK. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2017;8:20.
Woltering EA, Beyer DT, Thiagarajan R, et al. Elevated Plasma Pancreastatin, but Not Chromogranin A, Predicts Survival in Neuroendocrine Tumors of the Duodenum. J Am Coll Surg. 2016;222(4):534-42.
RATIONALE: The chromogranin A-derived peptide pancreastatin (PST) is a dysglycemic, counter-regulatory peptide for insulin action, especially in liver. Although previous evidence for a PST binding protein has been reported, such a receptor has not been identified or sequenced.
METHODS AND RESULTS: We used ligand affinity to purify the PST target, with biotinylated human PST (hCHGA273-301-amide) as “bait” and mouse liver homogenate as “prey”, and identified GRP78 (a.k.a. “78 kDa Glucose Regulated Protein”, HSPA5, BIP) as a major interacting partner of PST. GRP78 belongs to the family of heat shock proteins (chaperones), involved in several cellular processes including protein folding and glucose metabolism. We analyzed expression of GRP78 in the absence of PST in a mouse knockout model lacking its precursor CHGA: hepatic transcriptome data revealed global over-expression of not only GRP78 but also other heat shock transcripts (of the “adaptive UPR”) in CHGA(-/-) mice compared to wild-type (+/+). By contrast, we found a global decline in expression of hepatic pro-apoptotic transcripts in CHGA(-/-) mice. GRP78’s ATPase enzymatic activity was dose-dependently inhibited by PST (IC50∼5.2 µM). PST also inhibited the up-regulation of GRP78 expression during UPR activation (by tunicamycin) in hepatocytes. PST inhibited insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in adipocytes, and increased hepatic expression of G6Pase (the final step in gluconeogenesis/glycogenolysis). In hepatocytes not only PST but also other GRP78-ATPase inhibitors (VER-155008 or ADP) increased G6Pase expression. GRP78 over-expression inhibited G6Pase expression in hepatocytes, with partial restoration by GRP78-ATPase inhibitors PST, VER-155008, or ADP.
CONCLUSIONS: Our results indicate that an unexpected major hepatic target of PST is the adaptive UPR chaperone GRP78. PST not only binds to GRP78 (in pH-dependent fashion), but also inhibits GRP78’s ATPase enzymatic activity, and impairs its biosynthetic response to UPR activation. PST decreases insulin-stimulated cellular glucose uptake, and PST as well as other chaperone ATPase activity inhibitors augment expression of G6Pase; GRP78 over-expression antagonizes this PST action. Analysis of the novel PST/GRP78 interaction may provide a new avenue of investigation into cellular glycemic control as well as dysglycemia.
Biswas N, Friese RS, Gayen JR, Bandyopadhyay G, Mahata SK, O’connor DT. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(1):e84132.
This publication used the porcine pancreastatin RIA kit (RK-053-08) from Phoenix Pharmaceuticals for blood level measurement.
Frydland M, Kousholt B, Larsen JR, et al. Biomark Med. 2013;7(6):959-67.
This publication used a human pancreastatin peptide from Phoenix Pharmaceuticals for peptide level evaluation.
Giovinazzo F, Schimmack S, Svejda B, et al. Chromogranin A and its fragments as regulators of small intestinal neuroendocrine neoplasm proliferation. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(11):e81111.
CONCLUSIONS: Plasma CST level was positively correlated with that of NE and was elevated in parallel with that of NE in the different myocardial ischemia states. Plasma CST on admission was neither associated with adverse cardiac events nor was there any significant relationship between plasma CST and onset of new cardiovascular events. The pathophysiological role of CST in CHD needs further studies.
Liu L, Ding W, Zhao F, Shi L, Pang Y, Tang C. Scand Cardiovasc J. 2013;47(4):217-24.
Serum pancreastatin: the next predictive neuroendocrine tumor marker.
Rustagi S, Warner RR, Divino CM. J Surg Oncol. 2013 Aug;108(2):126-8. doi: 10.1002/jso.23359. Epub 2013 Jun 15.
Isolation and functional expression of human pancreatic peptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase.
Pancreastatin (PST) is processed from chromogranin A and the C-terminal amide of the peptide is an absolute requirement for biological activities. Human pancreatic carcinoma cells QGP-1 which produce both chromogranin A and PST were used to isolate cDNAs encoding two forms of peptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase (PAM). The two forms are a full length bifunctional enzyme and a variant lacking the transmembrane domain-coding region. When the cDNAs of these two forms were expressed in COS-7 cells, cells transfected with the predicted soluble form released into the culture medium a very much higher amidating activity which converts human chromogranin A-(273-302) to PST-29. The optimal pH for amidating activity was 5.4 and Cu2+, ascorbate and catalase were required as cofactors for the both forms of PAM. Km values for the membrane-bound and the soluble forms of PAM were 15.7 +/- 3.1 microM and 12.4 +/- 1.6 microM, respectively. These results demonstrate that both forms of PAM can function in the posttranslational processing of chromogranin A to PST in the environment of a secretory vesicle.
Tateishi K, Arakawa F, Misumi Y, Treston AM, Vos M, Matsuoka Y. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994;205(1):282-90.
Schematics