Atrial Natriuretic Peptide
Abstract
Cardiac natriuretic peptides: hormones with anticancer effects that localize to nucleus, cytoplasm, endothelium, and fibroblasts of human cancers.
Four cardiac peptide hormones, i.e., vessel dilator, long acting natriuretic peptide (LANP), kaliuretic peptide, and atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) synthesized by the same gene decrease within 24 hours up to 97% the number of human breast, colon, pancreatic, and prostate adenocarcinoma cells as well as human small-cell and squamous carcinomas of the lung cells. These peptide hormones completely inhibit the growth of human pancreatic adenocarcinomas growing in athymic mice. Immunocytochemical investigations have revealed that LANP, vessel dilator, kaliuretic peptide and ANP localize to the nucleus and cytoplasm of human pancreatic adenocarcinomas, which is consistent with their ability to decrease DNA synthesis in the nucleus of this cancer mediated by the intracellular messenger cyclic GMP. These peptide hormones also localize to the endothelium of capillaries and fibroblasts within these cancers. These are the first growth-inhibiting peptide hormones ever demonstrated to localize to the nucleus. Their ability to decrease the activation of growth promoting substances such as Extracellular Receptor Kinase (ERK)-1/2 and Nuclear Factor Kappa Beta (NFkappaB) suggests that in addition to inhibiting DNA synthesis their ability to decrease the activation of growth promoting substances helps to mediate their ability to inhibit the growth of human cancers.
Saba SR, Vesely DL. Cardiac natriuretic peptides: hormones with anticancer effects that localize to nucleus, cytoplasm, endothelium, and fibroblasts of human cancers. Histol Histopathol. 2006;21(7):775-83.
Natriuretic peptides and acute renal failure.
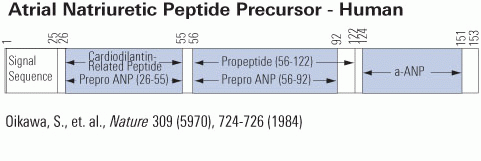
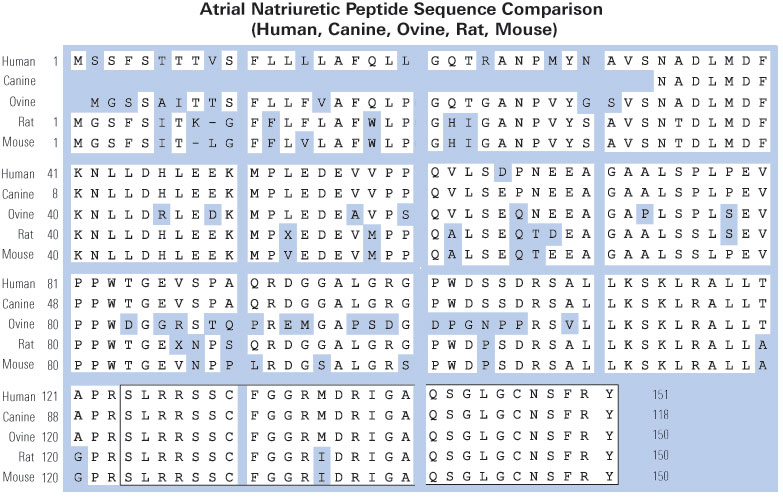
Atrial natriuretic peptides (ANPs) are a family of peptide hormones, e.g., ANP, long-acting natriuretic peptide, vessel dilator, and kaliuretic peptide synthesized by the ANP gene. Brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) and C-type natriuretic peptide are also members of this family but are synthesized by separate genes. Within the kidney, the ANP prohormone’s posttranslational processing is different from that of other tissues, resulting in an additional four amino acids added to the NH2 terminus of ANP (e.g., urodilatin). Each of these natriuretic and diuretic peptides increases within the circulation with acute renal failure (ARF). Renal transplantation but not hemodialysis returns their circulating concentrations to those of healthy individuals. BNP and adrenomedullin, a 52-amino acid natriuretic peptide, have beneficial effects on glomerular hypertrophy and glomerular injury but do not improve tubular injury (i.e., acute tubular necrosis). Vessel dilator ameliorates acute tubular necrosis with regeneration of the brush borders of proximal tubules. Vessel dilator decreases mortality in ARF from 88 to 14% at day 6 of ARF, even when given 2 days after renal failure has been established.
Vesely DL. Natriuretic peptides and acute renal failure. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2003;285(2):F167-77.
Schematics

More Information
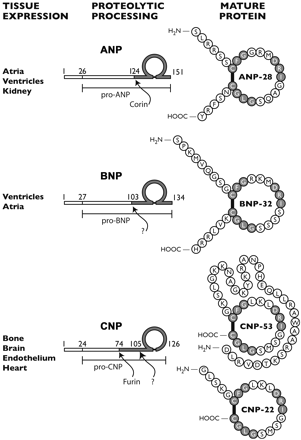 |
ANP is produced, stored and released by cardiac myocytes of the atria of the heart. It is released in response to atrial stretch and a variety of other signals induced by hypervolemia, exercise or caloric restriction. The hormone is constitutively expressed in the ventricle in response to stress induced by increased afterload (e.g. increased ventricular pressure from aortic stenosis) or injury (e.g. myocardial infarction).
ANP is secreted in response to:
The atria become distended by high extracellular fluid and blood volume, and atrial fibrillation. Notably, ANP secretion increases in response to immersion of the body in water, which causes atrial stretch due to an altered distribution of intravascular fluid. ANP secretion in response to exercise has also been demonstrated in horses.
|
