New Tumor Biomarker, Cardiovascular and Alzheimer-related Peptides
Abstract
CGRP induction in cystic fibrosis airways alters the submucosal gland progenitor cell niche in mice.
In cystic fibrosis (CF), a lack of functional CF transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) chloride channels causes defective secretion by submucosal glands (SMGs), leading to persistent bacterial infection that damages airways and necessitates tissue repair. SMGs are also important niches for slow-cycling progenitor cells (SCPCs) in the proximal airways, which may be involved in disease-related airway repair. Here, we report that calcitonin gene–related peptide (CGRP) activates CFTR-dependent SMG secretions and that this signaling pathway is hyperactivated in CF human, pig, ferret, and mouse SMGs. Since CGRP-expressing neuroendocrine cells reside in bronchiolar SCPC niches, we hypothesized that the glandular SCPC niche may be dysfunctional in CF. Consistent with this hypothesis, CFTR-deficient mice failed to maintain glandular SCPCs following airway injury. In wild-type mice, CGRP levels increased following airway injury and functioned as an injury-induced mitogen that stimulated SMG progenitor cell proliferation in vivo and altered the proliferative potential of airway progenitors in vitro. Components of the receptor for CGRP (RAMP1 and CLR) were expressed in a very small subset of SCPCs, suggesting that CGRP indirectly stimulates SCPC proliferation in a non-cell-autonomous manner. These findings demonstrate that CGRP-dependent pathways for CFTR activation are abnormally upregulated in CF SMGs and that this sustained mitogenic signal alters properties of the SMG progenitor cell niche in CF airways. This discovery may have important implications for injury/repair mechanisms in the CF airway.
Xie W, Fisher JT, Lynch TJ, et al. CGRP induction in cystic fibrosis airways alters the submucosal gland progenitor cell niche in mice. J Clin Invest. 2015;125(5):2179.
Breast density, scintimammographic (99m)Tc(V)DMSA uptake, and calcitonin gene related peptide (CGRP) expression in mixed invasive ductal associated with extensive in situ ductal carcinoma (IDC + DCIS) and pure invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC): correlation with estrogen receptor (ER) status, proliferation index Ki-67, and histological grade.
Papantoniou V, Sotiropoulou E, Valsamaki P, et al. Breast density, scintimammographic (99m)Tc(V)DMSA uptake, and calcitonin gene related peptide (CGRP) expression in mixed invasive ductal associated with extensive in situ ductal carcinoma (IDC + DCIS) and pure invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC): correlation with estrogen receptor (ER) status, proliferation index Ki-67, and histological grade. Breast Cancer. 2011;18(4):286-91.
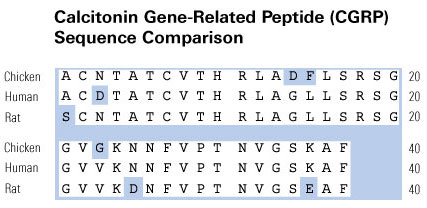
The calcitonin gene peptides: biology and clinical relevance.
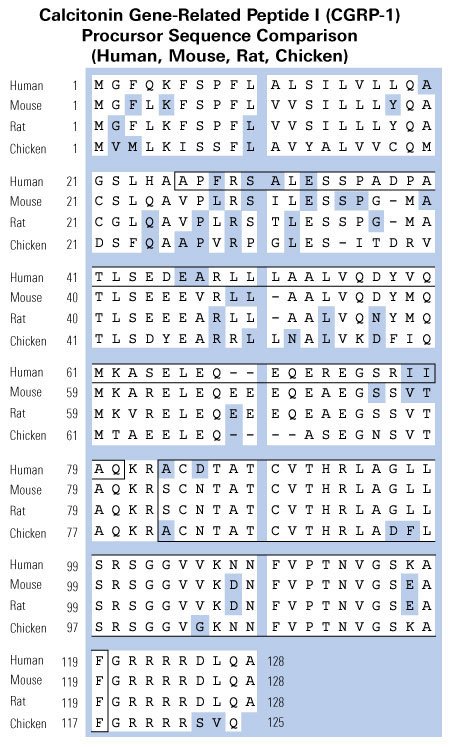
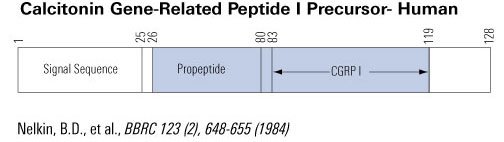
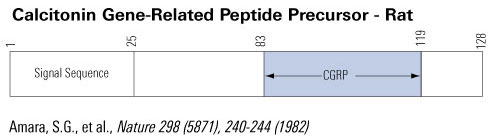
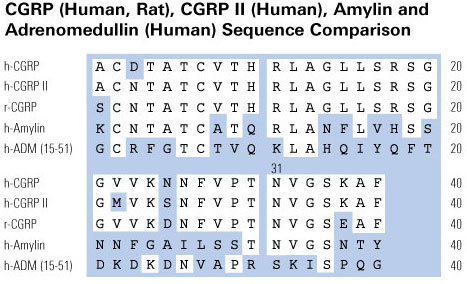
The calcitonin/CGRP multigene complex encodes a family of peptides: calcitonin, its C-terminal flanking peptide, katacalcin, and a third novel peptide, calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP). The 32-amino acid peptide calcitonin inhibits the osteoclast, thereby conserving skeletal mass during periods of potential calcium lack, such as pregnancy, growth, and lactation. This hormonal role is emphasized by observations that lower circulating calcitonin levels are associated with bone loss and that calcitonin replacement prevents further bone loss. Structurally, CGRP resembles calcitonin and has been implicated in neuromodulation and in the physiological regulation of blood flow. Here we review the molecular genetics, structure, and function of the calcitonin-gene peptides as analyzed in the laboratory and focus on more recent clinical studies relating to disorders and therapeutics.
Zaidi M, Moonga BS, Bevis PJ, Bascal ZA, Breimer LH. The calcitonin gene peptides: biology and clinical relevance. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 1990;28(2):109-74.
Schematics
   |
|