An insulin-like hormone
Abstract
Relaxin-like peptides in male reproduction – a human perspective.
Ivell R, Agoulnik AI, Anand-ivell R. Br J Pharmacol. 2017;174(10):990-1001.
Relaxin, its receptor (RXFP1), and insulin-like peptide 4 expression through gestation and in placenta accreta.
This study was designed to show whether placental relaxin (RLN), its receptor (RXFP1), or insulin-like peptide 4 (INSL4) might have altered expression in patients with placenta accreta. The baseline expression of their genes through gestation (n = 34) was quantitated in the placental basal plate (BP) and villous trophoblast (TR), and compared to their expression in placenta accreta (n = 6). The proteins were also immunolocalized and quantitated in the accreta tissues. The messenger RNAs (mRNAs) of matrix metalloproteinase 9, -2, and tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinase (TIMP)-1 were also measured. Results demonstrated that the BP and TR expressed low levels of RLN/RXFP1 and INSL4 through gestation. In accreta, increased RLN gene and protein in BP were associated with antepartum bleeding whereas INSL4 expression decreased throughout the TR. There were no changes in mRNAs for MMPs, but TIMP-1 was increased only in the invasive TR.
Goh W, Yamamoto SY, Thompson KS, Bryant-greenwood GD. Reprod Sci. 2013;20(8):968-80.
Changes in the maternal serum concentration of placenta insulin-like growth factor peptides in normal vs abnormal pregnancy.
CONCLUSION: These results showed that proEPIL secretion increases in the last trimester during normal pregnancy and is highly secreted in women with pathologic conditions.
Bruni L, Luisi S, Ferretti C, et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2007;197(6):606.e1-4.
Coevolution of the relaxin-like peptides and their receptors.
Wilkinson TN, Speed TP, Tregear GW, Bathgate RA. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005;1041:534-9.
[Expression of early placenta insulin-like growth factor (EPIL) in breast cancer cells provides an autocrine loop with enhancement of predominantly HER-2-related invasivity].
AIMS: Recently, we were able to show that the expression of early placenta insulin like growth factor (EPIL) is expressed by highly motile HER-2-positive breast cancer cells in vitro (Brandt et al., Cancer Res. 2002) in Paget cells in vivo and indicates a poor clinical prognosis, irrespectively of other prognostic factors.
METHODS: In order to demonstrate the interplay between HER-2 and Epil we established a cellular model for high simultaneous Epil and HER-2 expression. The HER-2-positive breast cancer cell line SKBR3 was modified with an EPIL expression vector. In addition, an assay for the knockdown of EPIL-expression via siRNA was established. Erk1/2 expression was measured via Western Blot. The phenotype of the viable cells was determined by laser scan microscopy.
RESULTS: Epil overexpression in SKBR3 cells resulted in fast and frequent protrusion formation of the cells shown by laser scan microscopy. The cells were further characterized by a significantly increased invasiveness, which could be reversed by Epil specific siRNA treatment. Increased invasiveness and morphological changes were associated with a decreased erk1/2 phosphorylation.
CONCLUSIONS: These data further supports the assumption that EPIL might provide an autocrine loop in HER-2-positive breast cancer cells that enforce metastasis, conceivably escape from adjuvant therapy and in consequence poor clinical outcome. A tight interaction between HER-2 and EPIL in invasive breast cancer cells is therefore likely. The exact mechanims remain to be elucidated.
Bürger H, Kemming D, Helms M, et al. Verh Dtsch Ges Pathol. 2005;89:201-6.
Molecular characterization and in vitro biological activity of placentin, a new member of the insulin gene family.
Insulin and insulin-like growth factors belong to a family of polypeptides involved in essential physiological processes. Placentin, a new member of the insulin family, was recently identified as a 139-amino acid open reading frame from a cDNA clone isolated from a subtracted library of first trimester human placenta. Tris/Tricine/SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and immunoblot analyses of histidine-tagged recombinant placentin indicate that it is composed of two peptide chains of apparent molecular masses of 4 and 13 kDa. Conditioned media produced by recombinant expression of placentin cDNA in the placental 3AsubE cell line were assayed for biological activity and found to stimulate tyrosine phosphorylation and DNA synthesis. While these effects closely mimicked those of insulin, they were not mediated by the insulin receptor as shown by the lack of tyrosine phosphorylation of this receptor upon placentin treatment. Moreover, in cytotrophoblast primary culture, production of chorionic gonadotropin, a marker of trophoblast differentiation, was increased upon treatment with placentin-conditioned media, while unaffected by insulin. These results suggest that placentin might participate in the cellular proliferation and/or differentiation processes during placental development.
Koman A, Cazaubon S, Couraud PO, Ullrich A, Strosberg AD. J Biol Chem. 1996;271(34):20238-41.
Cloning of a new member of the insulin gene superfamily (INSL4) expressed in human placenta.
A new member of the insulin gene superfamily was identified by screening a subtracted cDNA library of first-trimester human placenta and, hence, was tentatively named early placenta insulin-like peptide (EPIL). In this paper, we report the cloning and sequencing of the EPIL cDNA and the EPIL gene (INSL4). Comparison of the deduced amino acid sequence of the early placenta insulin-like peptide revealed significant overall and structural homologies with members of the insulin-like hormone superfamily. Moreover, the organization of the early placenta insulin-like gene, which is composed of two exons and one intron, is similar to that of insulin and relaxin. By in situ hybridization, the INSL4 gene was assigned to band p24 of the short arm of chromosome 9. RT-PCR analysis of EPIL tissue distribution revealed that its transcripts are expressed in the placenta and uterus.
Chassin D, Laurent A, Janneau JL, Berger R, Bellet D. Genomics. 1995;29(2):465-70.
Schematics
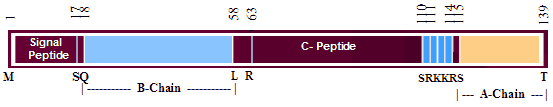
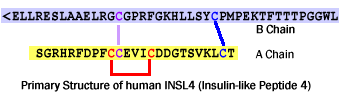

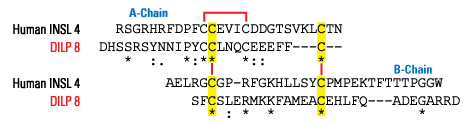
More Information
Serum levels of Prepro-INSL4 C-Peptide(64-110) (Human) measured using EIA Kit (EK-035-56)
| Type of samples
|
Measured Concentration (Mean ± S.D.) after using ½ X diluted sample in assay
|
|
Pregnant Women Serum (in-house samples N=26) |
28.09 ± 2.84 (ng/ml) |
|
Normal Human Serum (in-house samples N=7) |
17.85 ± 2.55 (ng/ml) |
|
Cord Blood (in-house samples N=21) |
7.85 ± 0.918 (ng/ml) |
