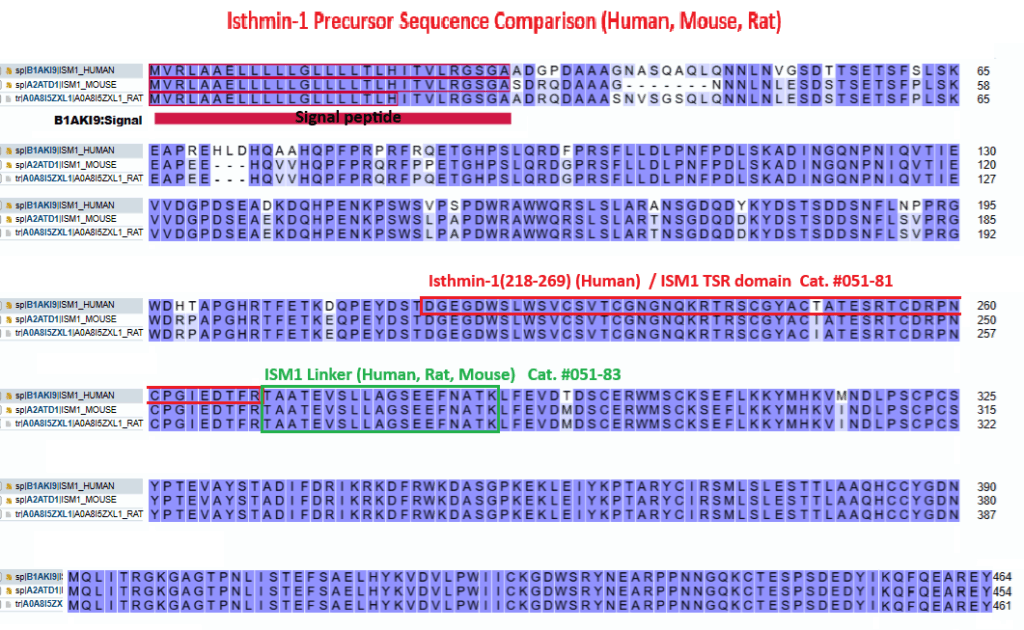
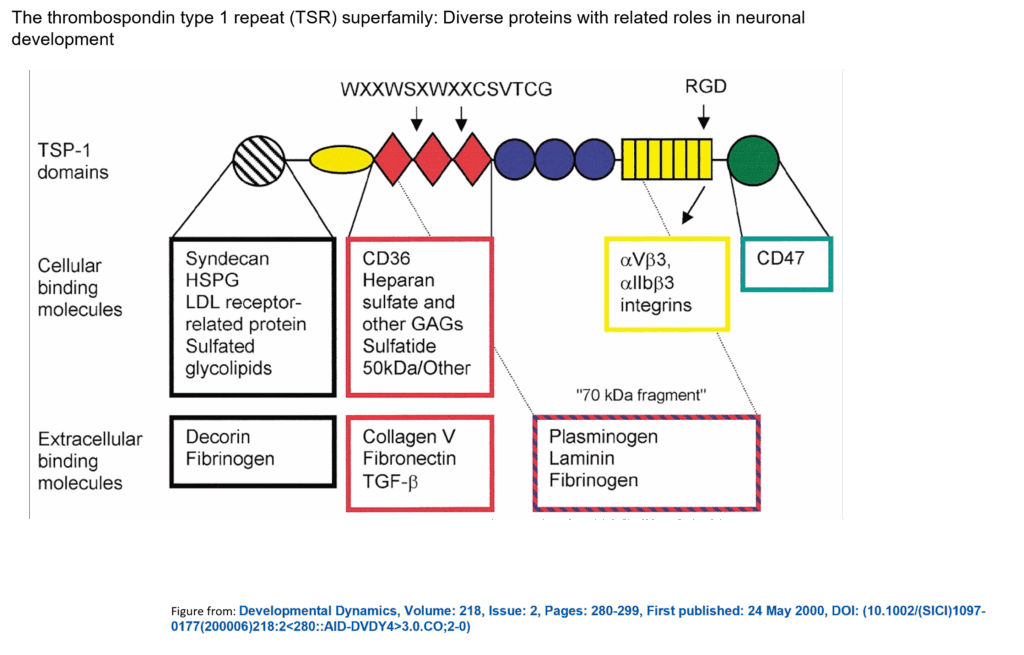
Ism1 secreted TSR peptide shows distinct multifunctional signaling actions
Abstract
Crystal structure of Isthmin-1 and reassessment of its functional role in pre-adipocyte signaling
Abstract: Isthmin-1 (ISM1) is a recently described adipokine with insulin-like properties that can control hyperglycemia and liver steatosis. Additionally, ISM1 is proposed to play critical roles in patterning, angiogenesis, vascular permeability, and apoptosis. A key feature of ISM1 is its AMOP (adhesion-associated domain in MUC4 (Mucin-4) and other proteins) domain which is essential for many of its functions. However, the molecular details of AMOP domains remain elusive as there are no descriptions of their structure. Here we determined the crystal structure
of ISM1 including its thrombospondin type I repeat (TSR) and AMOP domain. Interestingly, ISM1’s AMOP domain exhibits a distinct fold with similarities to bacterial streptavidin. When comparing our structure to
predicted structures of other AMOP domains, we observed that while the core streptavidin-like barrel is conserved, the surface helices and loops vary greatly. Thus, the AMOP domain fold allows for structural
plasticity that may underpin its diverse functions. Furthermore, and contrary to prior studies, we show that highly purified ISM1 does not stimulate AKT phosphorylation on 3T3-F442A pre-adipocytes. Rather, we find that co-purifying growth factors are responsible for this activity. Together, our data reveal the structure and clarify functional studies of this enigmatic protein.
Isthmin-1 is an adipokine that promotes glucose uptake and improves glucose
tolerance and hepatic steatosis
Abstract: With the increasing prevalence of type 2 diabetes and fatty liver disease, there is still an unmet need to better treat hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia. Here, we identify isthmin-1 (Ism1) as an adipokine and one that has a dual role in increasing adipose glucose uptake while suppressing
hepatic lipid synthesis. Ism1 ablation results in impaired glucose tolerance, reduced adipose glucose uptake, and reduced insulin sensitivity, demonstrating an endogenous function for Ism1 in glucose regulation. Mechanistically, Ism1 activates a PI3K-AKT signaling pathway independently of the insulin and insulin-like growth factor receptors. Notably, while the glucoregulatory function is shared with insulin, Ism1 counteracts lipid accumulation in the liver by switching hepatocytes from a lipogenic to a protein synthesis state. Furthermore, therapeutic dosing of recombinant Ism1 improves diabetes in diet-induced obese mice and ameliorates hepatic steatosis in a diet-induced fatty liver mouse model. These findings uncover an unexpected, bioactive protein hormone that might have simultaneous therapeutic potential for diabetes and fatty liver disease.
Phosphoproteomic mapping reveals distinct signaling actions and activation of muscle protein synthesis by Isthmin-1
Abstract: The secreted protein isthmin-1 (Ism1) mitigates diabetes by increasing adipocyte and skeletal muscle glucose uptake by activating the PI3K-Akt pathway. However, while both Ism1 and insulin converge on these common targets, Ism1 has distinct cellular actions suggesting divergence in downstream intracellular signaling pathways. To understand the biological complexity of Ism1 signaling, we performed phosphoproteomic analysis after acute exposure, revealing overlapping and distinct pathways of Ism1 and insulin. We identify a 53% overlap between Ism1 and insulin signaling and Ism1-mediated phosphoproteome-wide alterations in ~450 proteins that are not shared with insulin. Interestingly, we find several unknown phosphorylation sites on proteins related to protein translation, mTOR pathway, and, unexpectedly, muscle function in the Ism1 signaling network. Physiologically, Ism1 ablation in mice results in altered proteostasis, including lower muscle protein levels under fed and fasted conditions, reduced amino acid incorporation into proteins, and reduced phosphorylation of the key protein synthesis effectors Akt and downstream mTORC1 targets. As metabolic disorders such as diabetes are associated with accelerated loss of skeletal muscle protein content, these studies define a non-canonical mechanism by which this antidiabetic circulating protein controls muscle biology.
Schematics