Resistin, an adipocyte-derived cytokine, causes insulin resistance and glucose intolerance in mice
Abstract
Glucose intolerance and resistin expression in rat offspring exposed to ethanol in utero: modulation by postnatal high-fat diet.
High-fat diet and intrauterine growth retardation may predispose to obesity, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes. Because prenatal ethanol (ETOH) exposure causes intrauterine growth retardation, we investigated its interactions with postnatal high-fat diet on glucose tolerance and adipocyte-derived hormones in the rat offspring. High-fat-fed offspring had increased adiposity, serum leptin, and muscle uncoupling protein-3, but decreased adiponectin mRNA, compared with corresponding chow-fed groups. ETOH-exposed offspring had normal adiponectin, but increased resistin mRNA and protein, compared with controls, regardless of postnatal diet. Skeletal muscle glucose transporter-4 content was decreased after both ETOH exposure and high-fat feeding. Glycemic and insulin responses to an ip glucose challenge were equally increased in non-ETOH-exposed high-fat-fed offspring and in ETOH-exposed chow-fed offspring, with additive effects of ETOH and high-fat diet. Pancreatic insulin content was elevated only in non-ETOH-exposed high-fat-fed offspring. The data suggest that high-fat diet worsens glucose intolerance in offspring of rats exposed to ETOH. Prenatal ETOH exposure and postnatal high-fat diet might cause insulin resistance through separate mechanisms, involving resistin and adiponectin, respectively.
Chen L, Nyomba BL. Glucose intolerance and resistin expression in rat offspring exposed to ethanol in utero: modulation by postnatal high-fat diet. Endocrinology. 2003;144(2):500-8.
Increased resistin gene and protein expression in human abdominal adipose tissue.
Resistin, a novel signalling molecule isolated in mice has been suggested to be the putative hormone thought to link obesity with type 2 diabetes. The aim of this study was to examine resistin protein expression in human adipose tissue depots and resistin secretion in isolated adipose cells, to characterize resistin expression in human adipose tissue. Both resistin mRNA and protein expression were analysed from human adipose tissue (n = 45 adipose tissue samples: abdominal subcutaneous (Sc) n = 19, abdominal omental adipose tissue (Om) n = 10, thigh n = 9, breast n = 7). Resistin protein expression levels were similar in both the abdominal Sc and Om adipose tissue depots, and expression in abdominal fat depots were increased compared with thigh and breast tissue depots. These findings were consistent with the mRNA expression studies. Resistin was secreted from both pre-adipocytes and adipocytes cells. Thus, resistin resides within isolated adipose cells and is expressed and secreted in human adipose tissue. In conclusion, this study confirms the expression of resistin in human adipose tissue and increased expression in abdominal fat, this suggests a potential role in linking central obesity to type 2 diabetes and/or cardiovascular disease.
Mcternan PG, Mcternan CL, Chetty R, et al. Increased resistin gene and protein expression in human abdominal adipose tissue. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002;87(5):2407.
Schematics
More Information
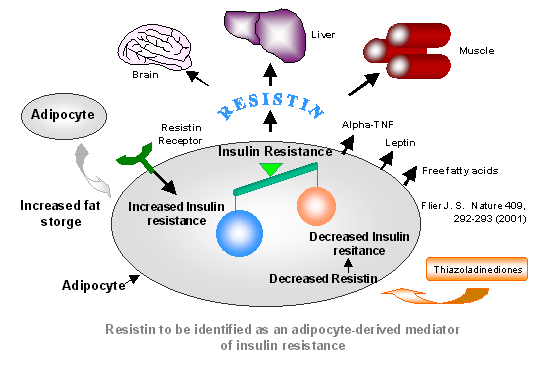
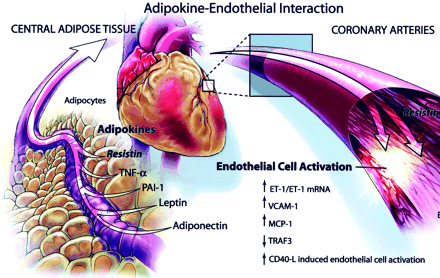
Illustrated model of adipokine–endothelial cell interaction. Adipocyte produces numerous hormones and cytokines such as TNF-{alpha}, plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 (PAI-1), leptin, adiponectin, and newly described molecule resistin. These factors play an important role locally (within adipose tissue) but may also have important effects as circulating bioactive factors. Ability of adipokines such as resistin to directly modulate endothelial function and incite endothelial activation may represent an important link between insulin resistance and cardiovascular disease.Verma S, et al. Circulation. 2003 Jul 21 [Epub ahead of print].