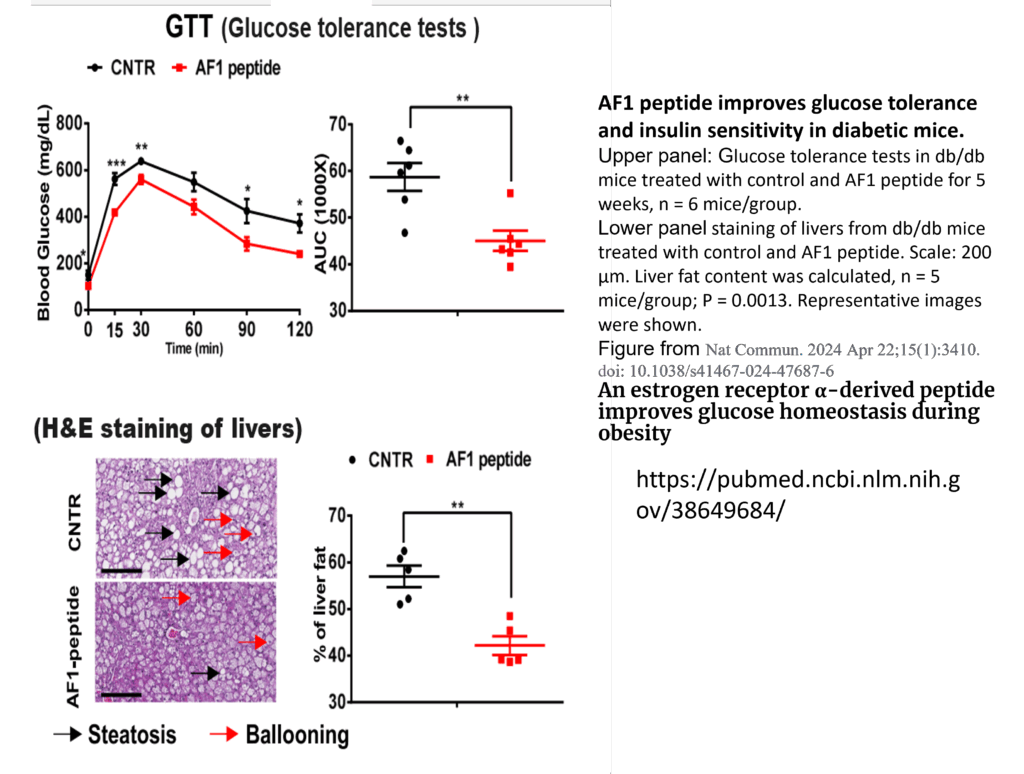
Estrogen alpha-derived peptide improves glucose homestasis in obese rats
Abstract
An estrogen receptor α-derived peptide improves glucose homeostasis during obesity
Abstract: Estrogen receptor α (ERα) plays a crucial role in regulating glucose and energy homeostasis during type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). However, the underlying mechanisms remain incompletely understood. Here we find a ligand-independent effect of ERα on the regulation of glucose homeostasis. Deficiency of ERα in the liver impairs glucose homeostasis in male, female, and ovariectomized (OVX) female mice. Mechanistic studies reveal that ERα promotes hepatic insulin sensitivity by suppressing ubiquitination-induced IRS1 degradation. The ERα 1-280 domain mediates the ligand-independent effect of ERα on insulin sensitivity. Furthermore, we identify a peptide based on ERα 1-280 domain and find that ERα-derived peptide increases IRS1 stability and enhances insulin sensitivity. Importantly, administration of ERα-derived peptide into obese mice significantly improves glucose homeostasis and serum lipid profiles. These findings pave the way for the therapeutic intervention of T2DM by targeting the ligand-independent effect of ERα and indicate that ERα-derived peptide is a potential insulin sensitizer for the treatment of T2DM.
Future therapeutic perspectives in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a focus on nuclear receptors, a promising therapeutic target
Abstract: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a major public health problem worldwide, with an increasing incidence, secondary to the increasing incidence of obesity and diabetes, from a very young age. It is associated with metabolic and cardiovascular disorders, as components of the metabolic syndrome (MS). NAFLD is the hepatic manifestation of MS. The pathogenesis of the disease is multifactorial and complex, involving genetic, metabolic, but also environmental factors. Currently, nuclear receptors (NRs) represent a promising therapeutic target in the treatment of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Of these, the most studied receptor was the liver X receptor (LXR), which would have great potential in the treatment of metabolic diseases, namely hypercholesterolemia, atherosclerosis, and NAFLD. However, the therapeutic use of NRs is restricted in medical practice for two reasons: limited knowledge of the structure of the receptor and its inability to modulate certain actions in the target organs and genes. One problem is the understanding of the function and structure of the N-terminal domain which has a major transcriptional activation function (AF1).
Schematics