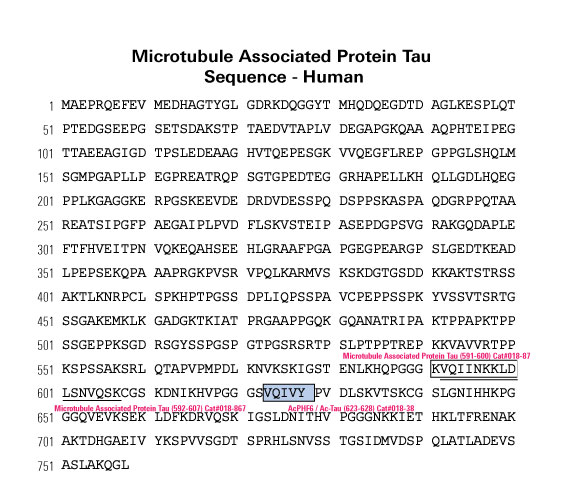
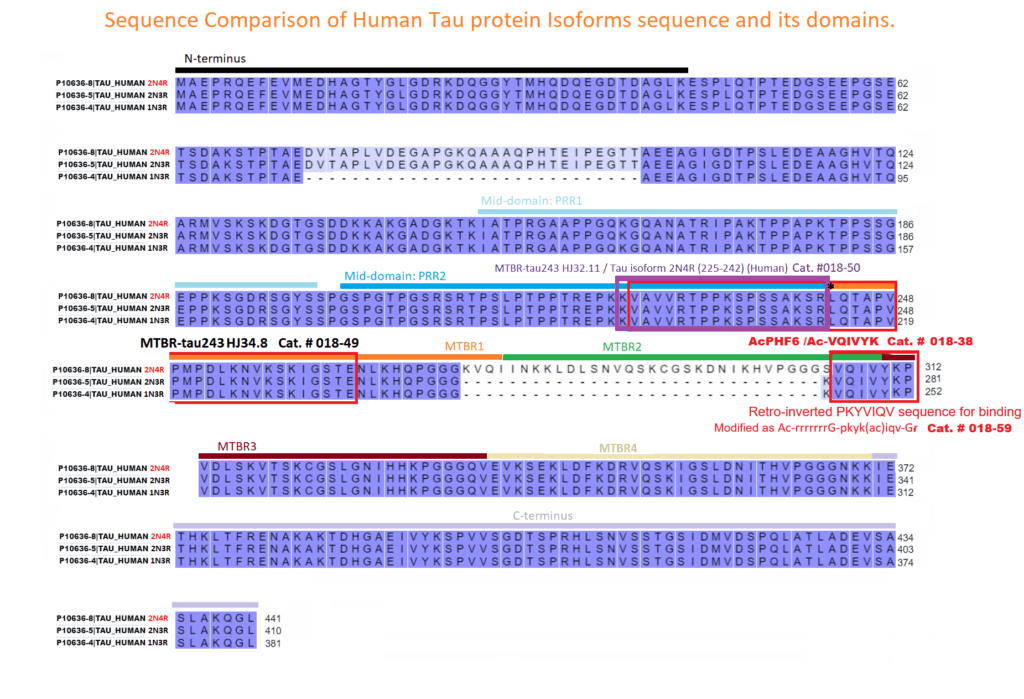
Tau protein discovery is a top priority in AD studies
Abstract
A novel peptide-based tau aggregation inhibitor as a potential therapeutic for Alzheimer’s disease and other tauopathies
Introduction: As aggregation underpins Tau toxicity, aggregation inhibitor peptides may have disease-modifying potential. They are therefore currently being designed and target either the 306VQIVYK311 aggregation-promoting hotspot found in all Tau isoforms or the 275VQIINK280 aggregation-promoting hotspot found in 4R isoforms. However, for any Tau aggregation inhibitor to potentially be clinically relevant for other tauopathies, it should target both hotspots to suppress aggregation of Tau isoforms, be stable, cross the blood-brain barrier, and rescue aggregation-dependent Tau phenotypes in vivo.
Methods: We developed a retro-inverso, stable D-amino peptide, RI-AG03 [Ac-rrrrrrrrGpkyk(ac)iqvGr-NH2], based on the 306VQIVYK311 hotspots which exhibit these disease-relevant attributes.
Results: Unlike other aggregation inhibitors, RI-AG03 effectively suppresses aggregation of multiple Tau species containing both
hotspots in vitro and in vivo, is non-toxic, and suppresses aggregation-dependent neurodegenerative and behavioral phenotypes.
Discussion: RI-AG03 therefore meets many clinically relevant requirements for an anti-aggregation Tau therapeutic and should be
explored further for its disease-modifying potential for Tauopathies.
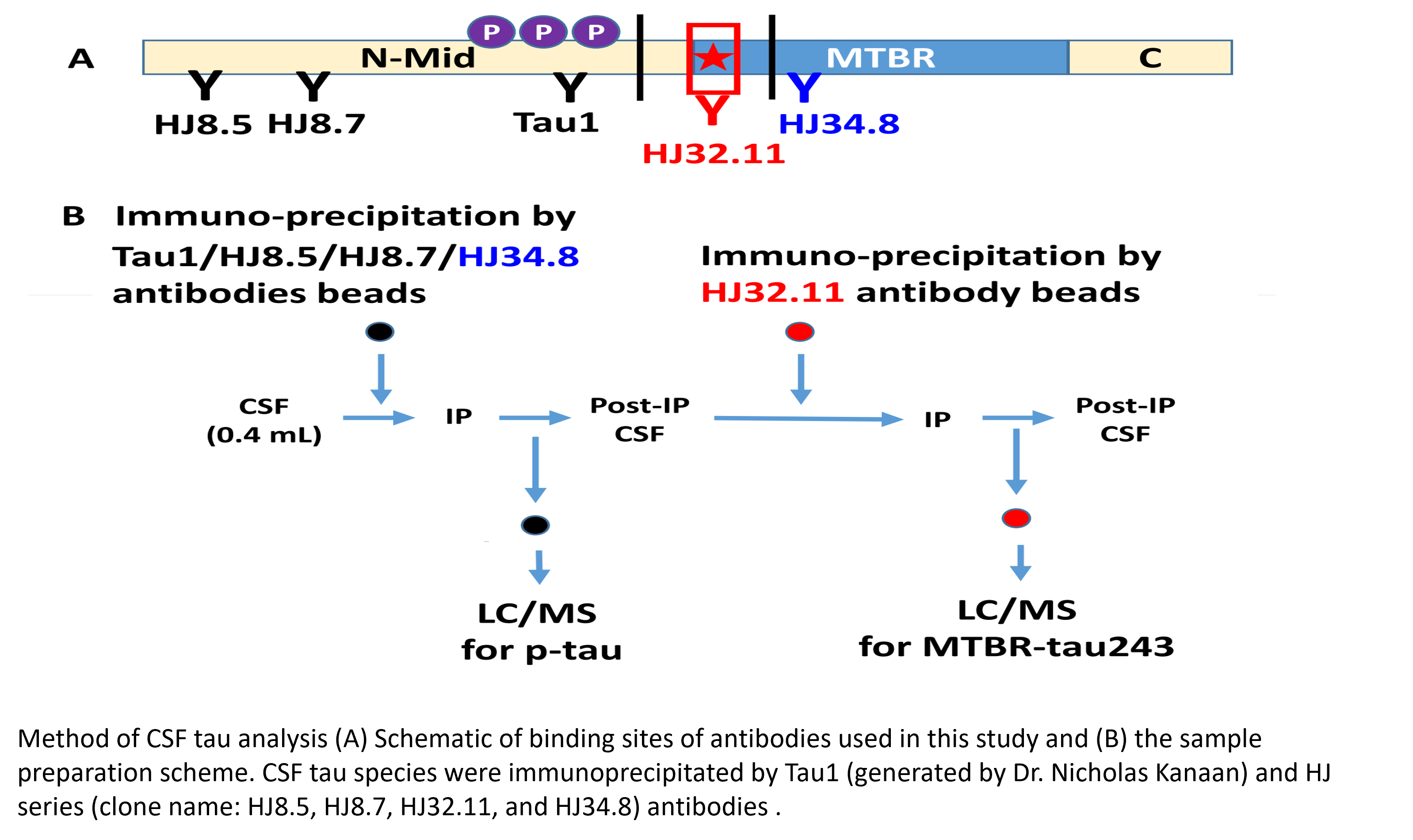
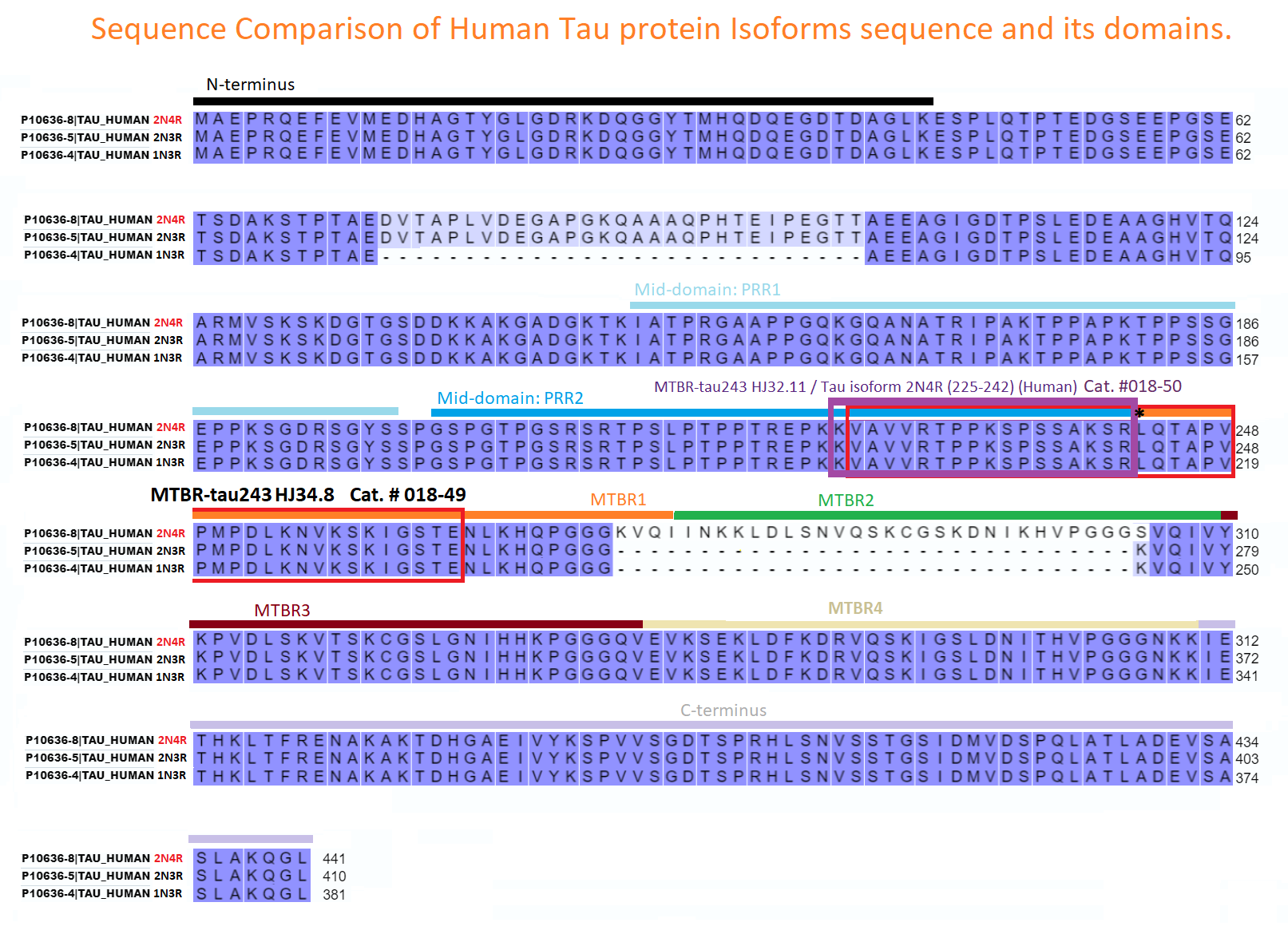
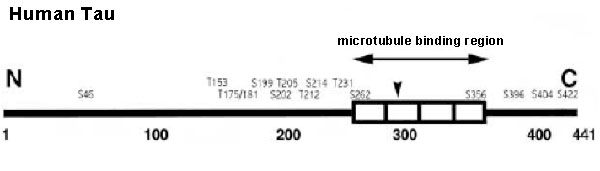
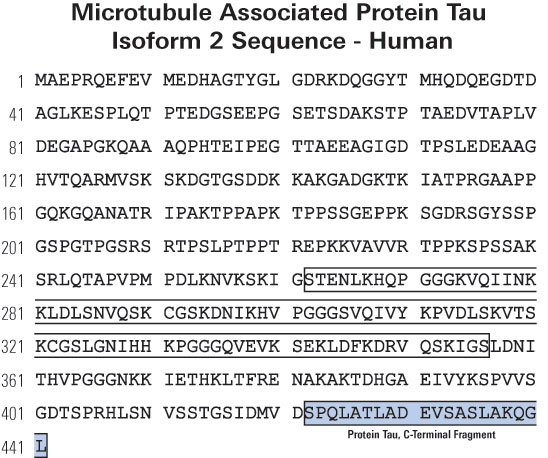
CSF MTBR-tau243 is a specific biomarker of tau tangle pathology in Alzheimer’s disease
Horie K, Salvadó G, Barthélemy NR, et al. CSF MTBR-tau243 is a specific biomarker of tau tangle pathology in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Med. Published online July 13, 2023.
CSF tau microtubule binding region identifies tau tangle and clinical stages of Alzheimer’s disease
Horie K, Barthélemy NR, Sato C, Bateman RJ. CSF tau microtubule binding region identifies tau tangle and clinical stages of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain. 2021;144(2):515-527.
Tauopathies feature progressive accumulation of tau amyloids. Pathology may begin when these amplify from a protein template, or seed, whose structure is unknown. We have purified and characterized distinct forms of tau monomer-inert (Mi) and seed-competent (Ms). Recombinant Ms triggered intracellular tau aggregation, induced tau fibrillization in vitro, and self-assembled. Ms from Alzheimer’s disease also seeded aggregation and self-assembled in vitro to form seed-competent multimers. We used crosslinking with mass spectrometry to probe structural differences in Mi vs. Ms. Crosslinks informed models of local peptide structure within the repeat domain which suggests relative inaccessibility of residues that drive aggregation (VQIINK/VQIVYK) in Mi, and exposure in Ms. Limited proteolysis supported this idea. Although tau monomer has been considered to be natively unstructured, our findings belie this assumption and suggest that initiation of pathological aggregation could begin with conversion of tau monomer from an inert to a seed-competent form.
Mirbaha H, Chen D, Morazova OA, et al. Inert and seed-competent tau monomers suggest structural origins of aggregation. Elife. 2018;7
Aggregated tau protein is associated with over 20 neurological disorders, which include Alzheimer’s disease. Previous work has shown that tau’s sequence segments VQIINK and VQIVYK drive its aggregation, but inhibitors based on the structure of the VQIVYK segment only partially inhibit full-length tau aggregation and are ineffective at inhibiting seeding by full-length fibrils. Here we show that the VQIINK segment is the more powerful driver of tau aggregation. Two structures of this segment determined by the cryo-electron microscopy method micro-electron diffraction explain its dominant influence on tau aggregation. Of practical significance, the structures lead to the design of inhibitors that not only inhibit tau aggregation but also inhibit the ability of exogenous full-length tau fibrils to seed intracellular tau in HEK293 biosensor cells into amyloid. We also raise the possibility that the two VQIINK structures represent amyloid polymorphs of tau that may account for a subset of prion-like strains of tau.
Seidler PM, Boyer DR, Rodriguez JA, et al. Structure-based inhibitors of tau aggregation. Nat Chem. 2018;10(2):170-176.
BACKGROUND: Ideally, disease modifying therapies for Alzheimer disease (AD) will be applied during the ‘preclinical’ stage (pathology present with cognition intact) before severe neuronal damage occurs, or upon recognizing very mild cognitive impairment. Developing and judiciously administering such therapies will require biomarker panels to identify early AD pathology, classify disease stage, monitor pathological progression, and predict cognitive decline. To discover such biomarkers, we measured AD-associated changes in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) proteome.
METHODS AND FINDINGS: CSF samples from individuals with mild AD (Clinical Dementia Rating [CDR] 1) (n = 24) and cognitively normal controls (CDR 0) (n = 24) were subjected to two-dimensional difference-in-gel electrophoresis. Within 119 differentially-abundant gel features, mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) identified 47 proteins. For validation, eleven proteins were re-evaluated by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA). Six of these assays (NrCAM, YKL-40, chromogranin A, carnosinase I, transthyretin, cystatin C) distinguished CDR 1 and CDR 0 groups and were subsequently applied (with tau, p-tau181 and Aβ42 ELISAs) to a larger independent cohort (n = 292) that included individuals with very mild dementia (CDR 0.5). Receiver-operating characteristic curve analyses using stepwise logistic regression yielded optimal biomarker combinations to distinguish CDR 0 from CDR>0 (tau, YKL-40, NrCAM) and CDR 1 from CDR<1 (tau, chromogranin A, carnosinase I) with areas under the curve of 0.90 (0.85-0.94 95% confidence interval [CI]) and 0.88 (0.81-0.94 CI), respectively.